vol. 5 6/2016 Inżynier i Fizyk Medyczny
318
artykuł
\
article
radioterapia
\
radiotherapy
INTRODUCTION
PDR (Pulsed Dose Rate) brachytherapy treatment is a radiothe-
rapy modality combining physical advantages of HDR brachy-
therapy (dose distribution optimization as well as radiation
safety) with radiobiological equivalency of LDR (Low Dose Rate)
brachytherapy. At the beginning of the 90’s, a new technique
was developed in order to mimic the radiobiological effect of
continuous LDR, while taking advantage of the same stepping
source technology developed for HDR (High Dose Rate) brachy-
therapy. Source strength was reduced from about 1 Ci (instead
of 10 Ci). The total dose delivered is approximately the same as
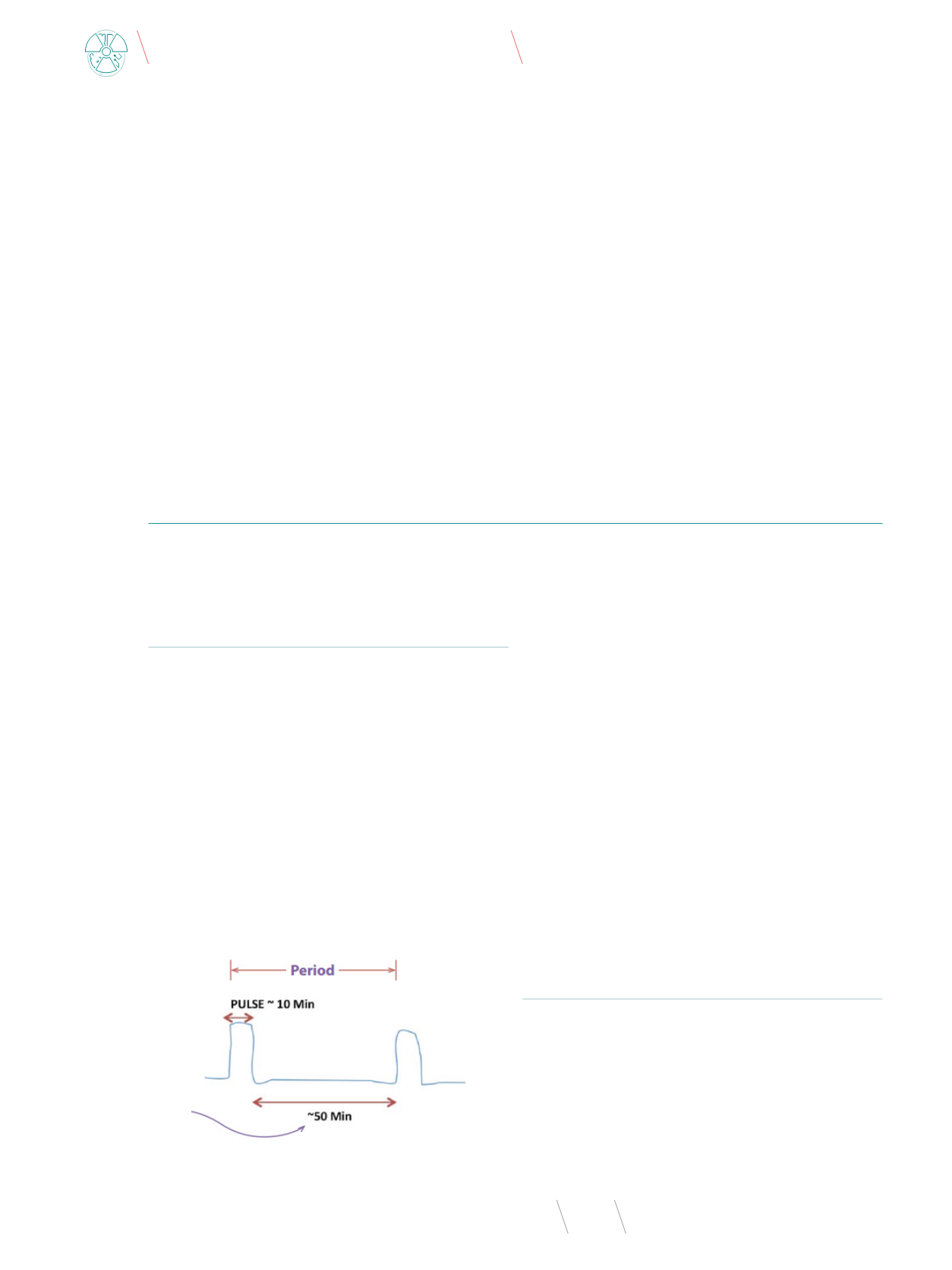
with continuous LDR. It is provided with a large number of small
fractions (or pulses), lasting usually 10 to 30 minutes, typically
one per hour, up to one per 4 hours (Fig. 1).
PDR uses an Iridium-192 radiation source. The main advan-
tage of PDR is a modern afterloading system offering over in-
terstitial or intracavitary insertion of separate needles, tubes,
seeds or wires. A dose distribution can be modulated flexibly to
fit it to the treated volume (HRV/IRV) as well as OARs’ (organ at
risk) constraints. This can be realised by setting dwell positions
of a radioactive source, adjusting dwell times and by a combina-
tion of positioning of catheters, applicators and another types
of interest. PDR brachytherapy and “pulse scheme” of building
a dose distribution allows only for incomplete repair, aiming at
achieving a radiobiological effect similar to low dose rate over
the same treatment time, typically a few days. The radiation so-
urce is removed into a shielded safe after completing the each
pulse what eliminates “environmental” radiation exposures and
decreases a risk of delivery of an unintended dose to staff and
visitors.
PDR TREATMENT – CERVICAL CANCER
Brachytherapy is an integral part of radical therapy for cervical
cancer. While image-based planning has gained wide acceptan-
ce in external beam radiotherapy, the integration of image-ba-
sed planning for brachytherapy has lagged significantly. More
recently advances in planning software/hardware have a lead to
increased use of image-based brachytherapy.
In NX Hospital, it is currently based on CT and MRI 3D images
taken for a patient with inserted applicator/catheter/BT inserts
Implementation of an independent
radiation detector actively monitoring
delivery of radiation pulses during
gynaecological PDR brachytherapy
treatment
Tervinder Matharu
1
, Dominika Oborska-Kumaszynska
1
, Tim Allen
1
, Christina Stewart
2
, Rose Cox
1
,
Ernie Dalton
1
, Malcolm Foley
1
1
The Royal Wolverhampton NHS Trust New Cross hospital Wednesfield, Wolverhampton WV10 0QP, United Kingdom, e-mail:
2
Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh NHS Lothian, Edinburgh, United Kingdom
Fig. 1
. The PDR treatment idea
Source: [4].


